Carbon Materials & Graphite
Carbon Materials & Graphite — Structure, Order, and Potential
Carbon materials are not defined by their elemental composition.
They are defined by structure—how carbon atoms organize themselves across length scales, from nanometric domains to macroscopic morphology.
This organisation determines conductivity, mechanical behaviour, reactivity, surface chemistry, and ultimately performance in industrial applications.
Microscopy and spectroscopy reveal the trajectory of carbon, not merely its current state.
Natural precursors are not equal
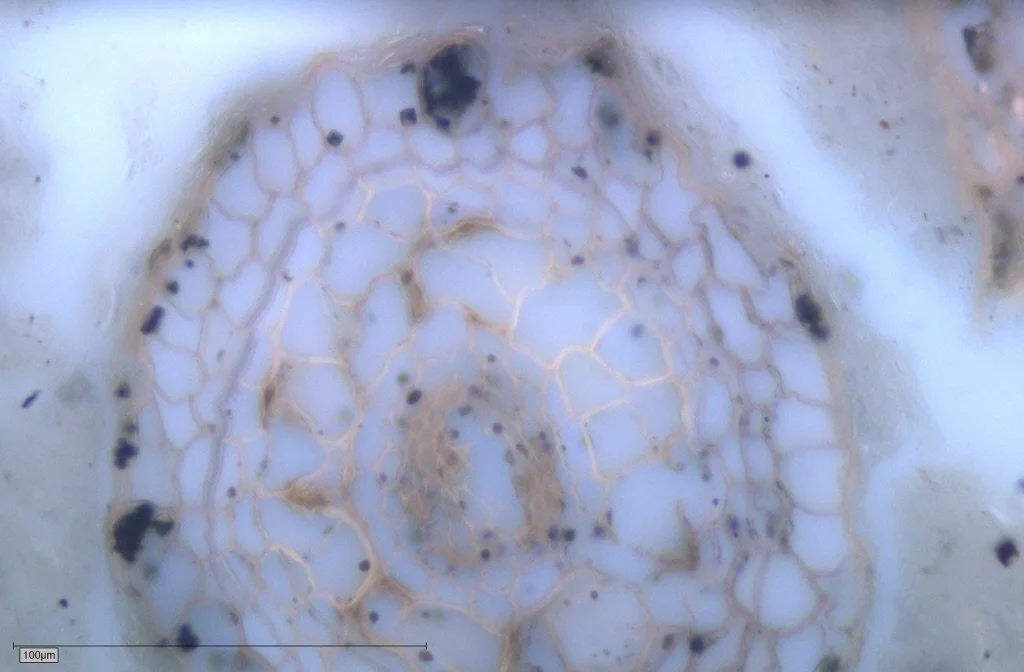
Anthracite, semi-graphite, and graphite may share carbon percentages, yet they are not interchangeable.
Their microstructure retains memories of:
precursor biological architecture (vitrinite, inertinite, liptinite)
tectonic strain and compaction
devolatilisation pathways
fluid interaction
catalytic vs non-catalytic graphitisation
weathering and oxidation
These histories manifest as distinct domain size distributions, stacking order, and turbostratic defects, which control how a material responds to heat, pressure, or electrochemical cycling.
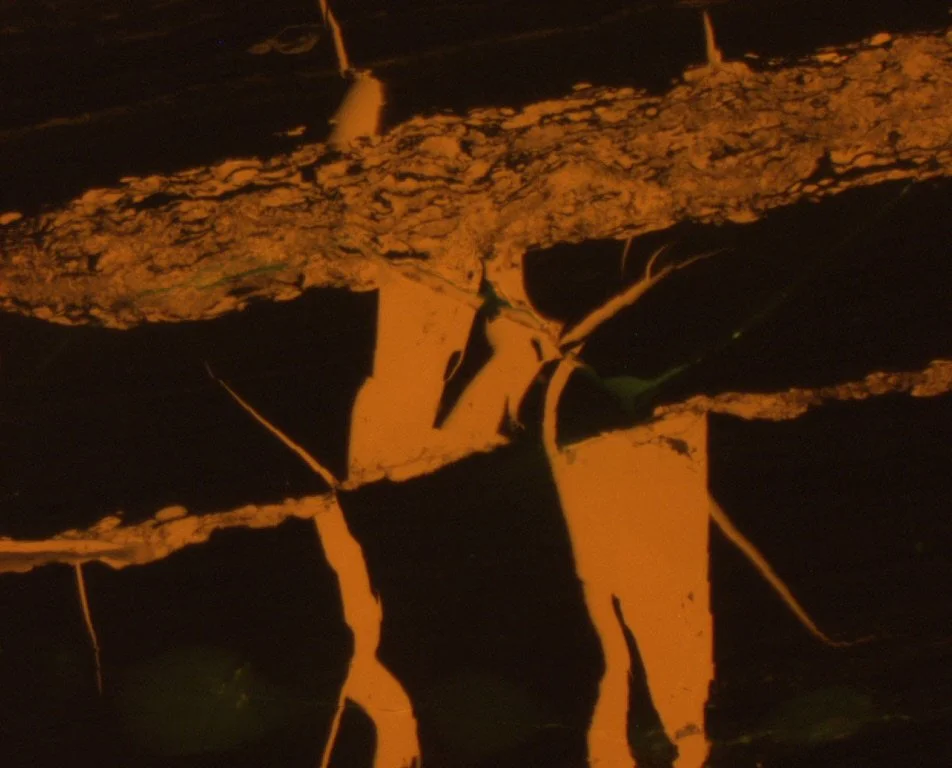
Natural Graphite. Canada. Photomicrograph taken with reflected white light and lambda plate.
Graphitisation is a process, not a label
The term “graphite” is often applied loosely.
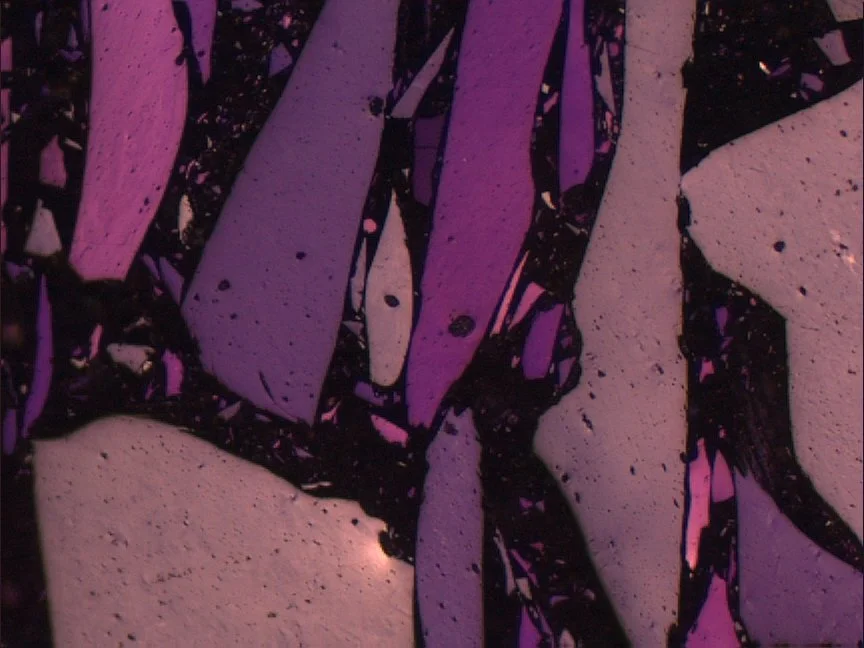
At the microscopic scale, most “graphite” encountered in natural or synthetic contexts is turbostratic carbon: layered but rotationally disordered.
True graphitisation requires:
lateral domain growth
basal plane alignment
decrease in defect density
reduction of heteroatom interference
collapse of cross-linking residuals
Raman and XRD do not simply “identify graphite”— they quantify how close a material is to acting like one.
Synthetic graphite. Photomicrograph taken with reflected white light and lambda plate.
What CarbonMat evaluates
We characterise structure using a complementary set of methods:
Raman spectroscopy: disorder, crystallite size (La, Lc), band ratios and widths
XRD: interlayer spacing (d₀₀₂), stacking order, graphitic vs turbostratic indices
Optical microscopy: inherited textures, precursor macerals, carbonisation pathways
SEM/EDS (where relevant): porosity, morphology, mineral residues
These datasets are integrated—not treated as isolated metrics—to determine the trajectory of your material, not merely its label.
Natural semigraphite. Kaiserberg, Austria. Photomicrograph taken with reflected white light and lambda plate.
Why interpretation matters
Two samples with identical carbon >90% cannot be assumed to behave the same way.
Their microstructural inheritance controls:
thermal conversion routes
suitability as anode precursor
catalytic response during graphitisation
oxidation resistance
mechanical integrity in composites
propensity to produce CNT/CNF during processing
success or failure in scale-up
Bulk chemistry will not warn you of failure. Microstructure will.
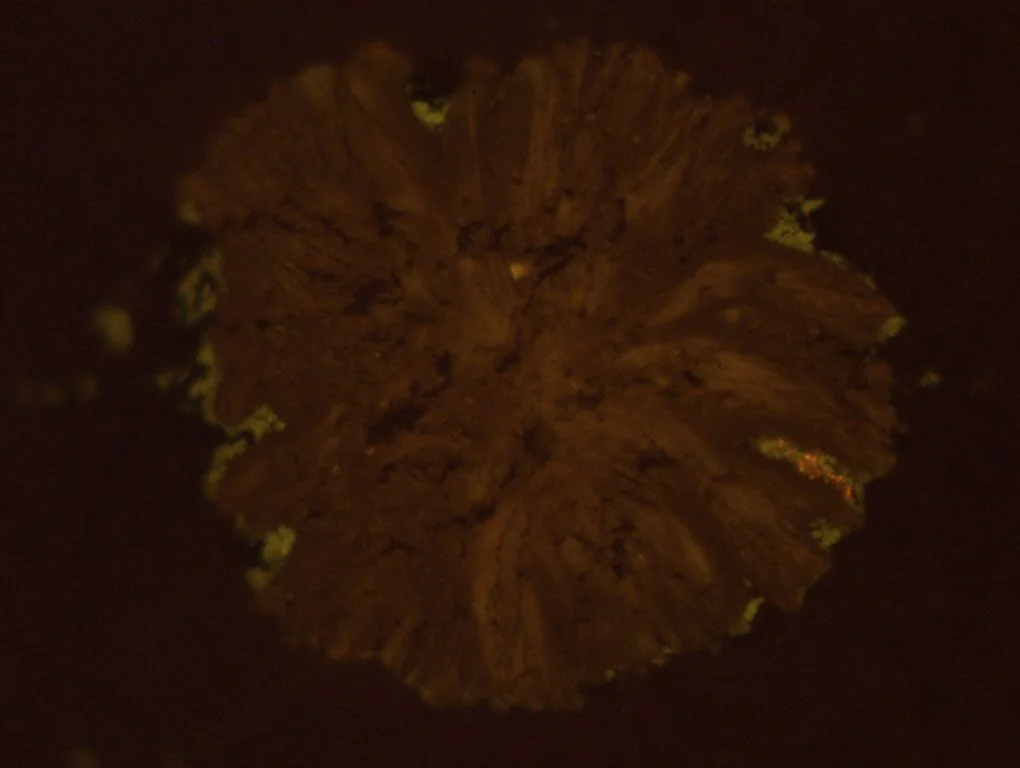
Char from coal. Photomicrograph taken with reflected white light and lambda plate.
Applications we support
Anode material development
Alternative carbon precursors for battery technologies
Electrode performance optimisation
High-temperature carbon products (furnaces, refractories, crucibles)
Research and pilot plant programs
Academic collaborations
You receive:
quantitative datasets
microstructural interpretation
implications for processing route selection
Work with CarbonMat
what material you have,
what you want it to become,
the constraints of your process.
CarbonMat will determine the most effective analytical pathway to evaluate its potential.
High temparature treatment (2500°C) of a meta-anthracite from Douro Basin, Portugal. Photomicrograph taken with reflected white light and lambda plate.
Natural materials as high-value precursors
Coal-derived carbons, anthracite, semi-coke, and pyrolytic products are increasingly strategic.
Their advantage lies not in purity, but in pre-existing structural ordering that industrial synthesis cannot easily replicate.
Understanding these architectures is the difference between:
a precursor that graphitises at 2700°C
andone that graphitises at 3100°C, or not at all.
CarbonMat assesses why.